IJMS, Free Full-Text
IJMS, Free Full-Text
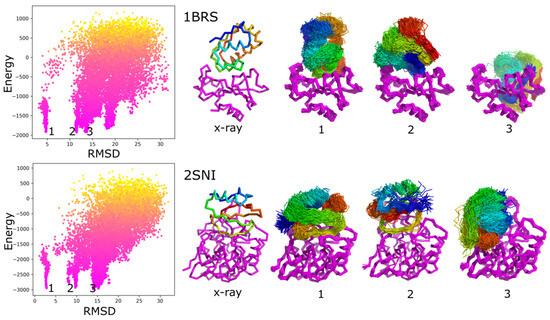
Most of the protein–protein docking methods treat proteins as almost rigid objects. Only the side-chains flexibility is usually taken into account. The few approaches enabling docking with a flexible backbone typically work in two steps, in which the search for protein–protein orientations and structure flexibility are simulated separately. In this work, we propose a new straightforward approach for docking sampling. It consists of a single simulation step during which a protein undergoes large-scale backbone rearrangements, rotations, and translations. Simultaneously, the other protein exhibits small backbone fluctuations. Such extensive sampling was possible using the CABS coarse-grained protein model and Replica Exchange Monte Carlo dynamics at a reasonable computational cost. In our proof-of-concept simulations of 62 protein–protein complexes, we obtained acceptable quality models for a significant number of cases.
Ijms Free Full Text The Macrophages Microbiota Interplay In Irasutoya

IJMS, Free Full-Text
IJMS, Free Full-Text
IJMS, Free Full-Text
IJMS, Free Full-Text
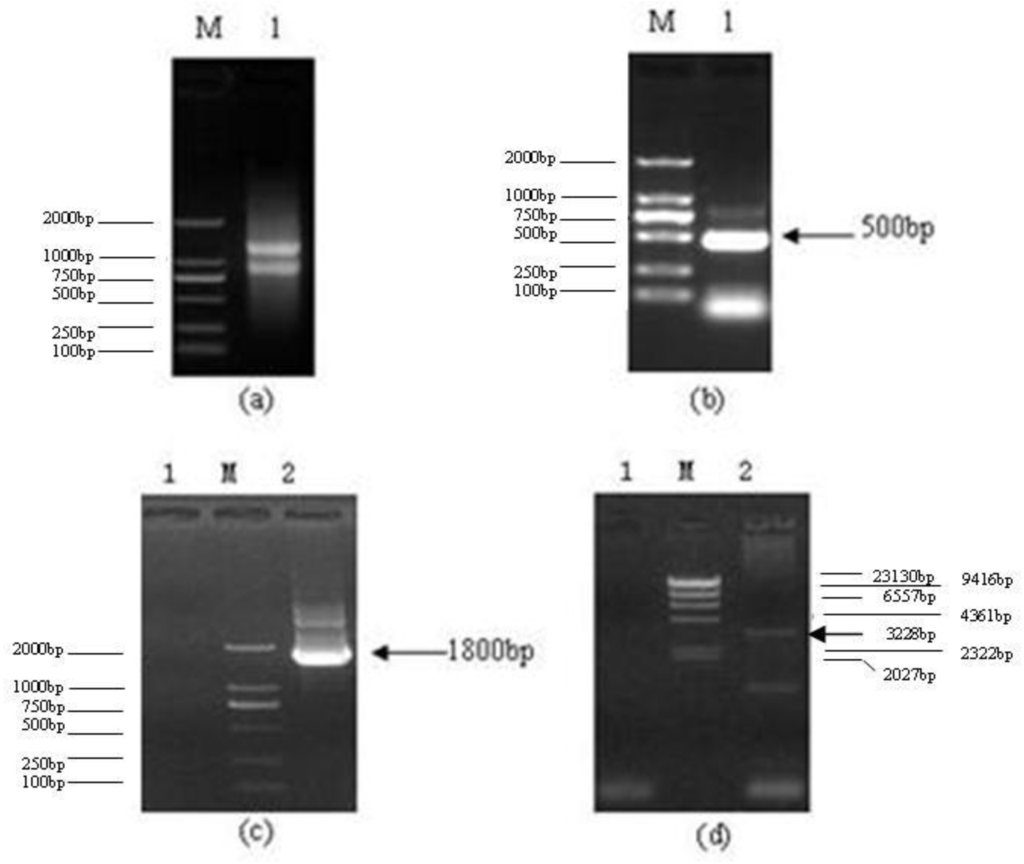
IJMS, Free Full-Text
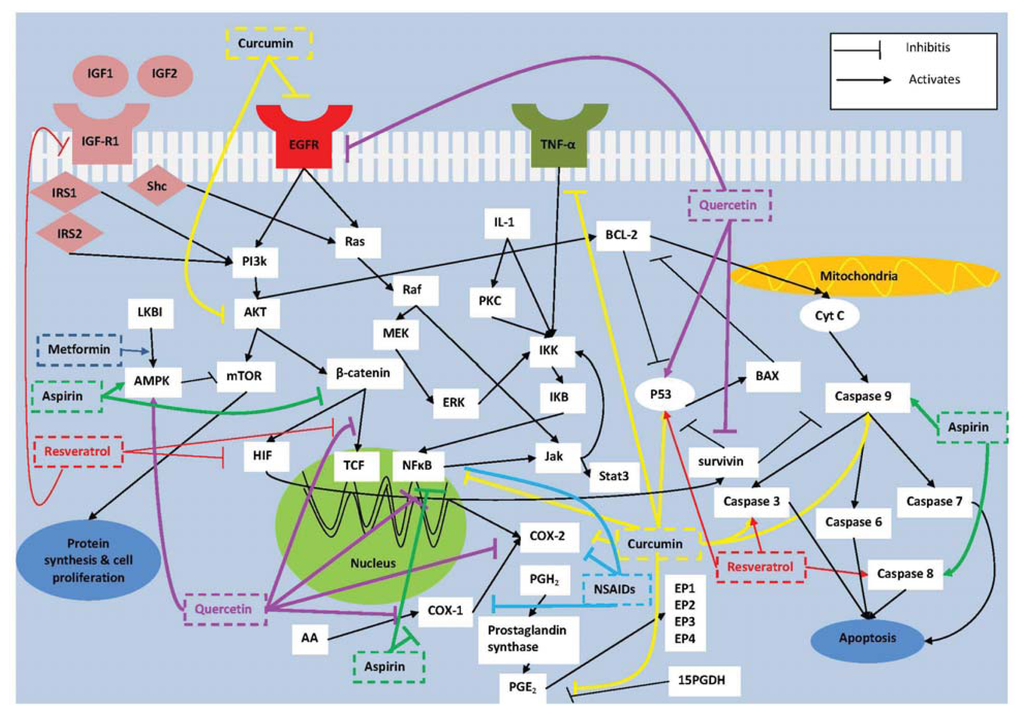
IJMS, Free Full-Text
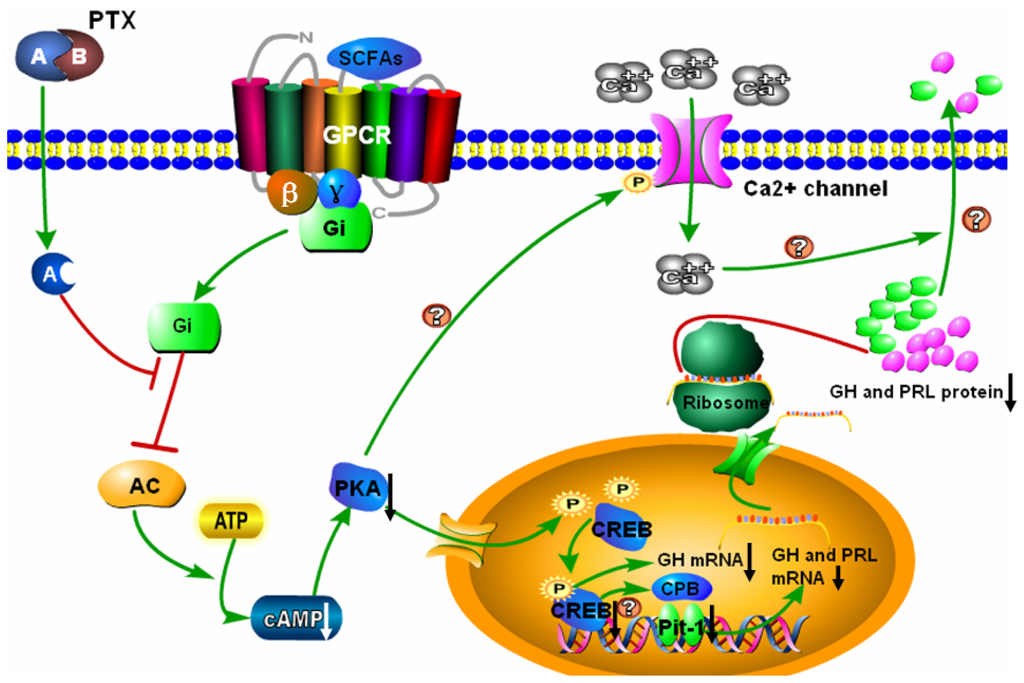
pka creb signaling pathway - Clip Art Library
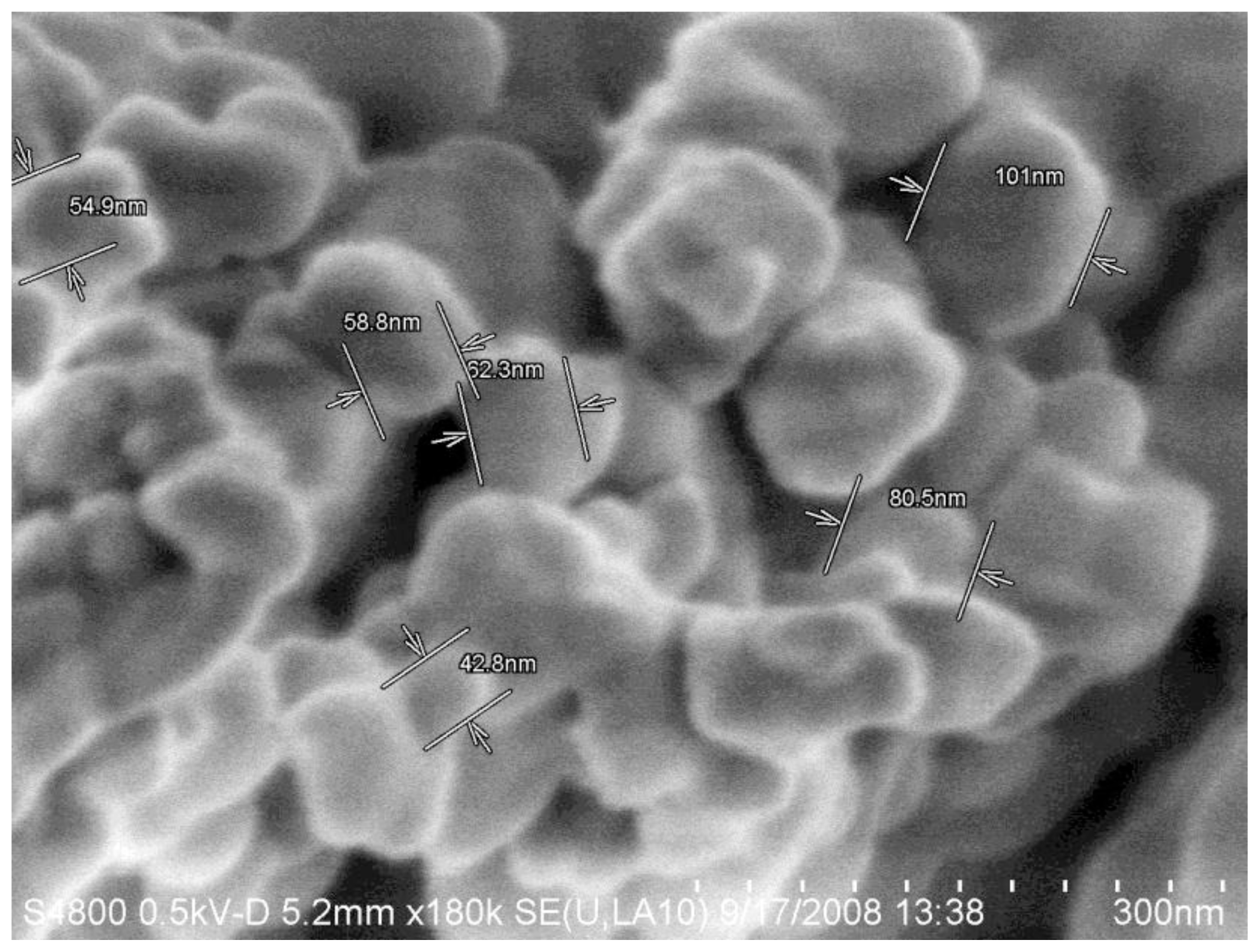
Ijms Free Full Text Influence Of Dose On Particle Size And Optical Properties Of Colloidal 80730
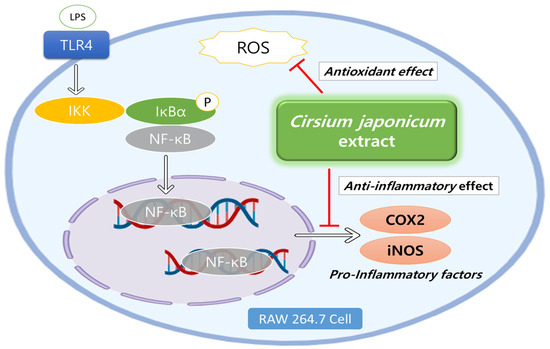
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
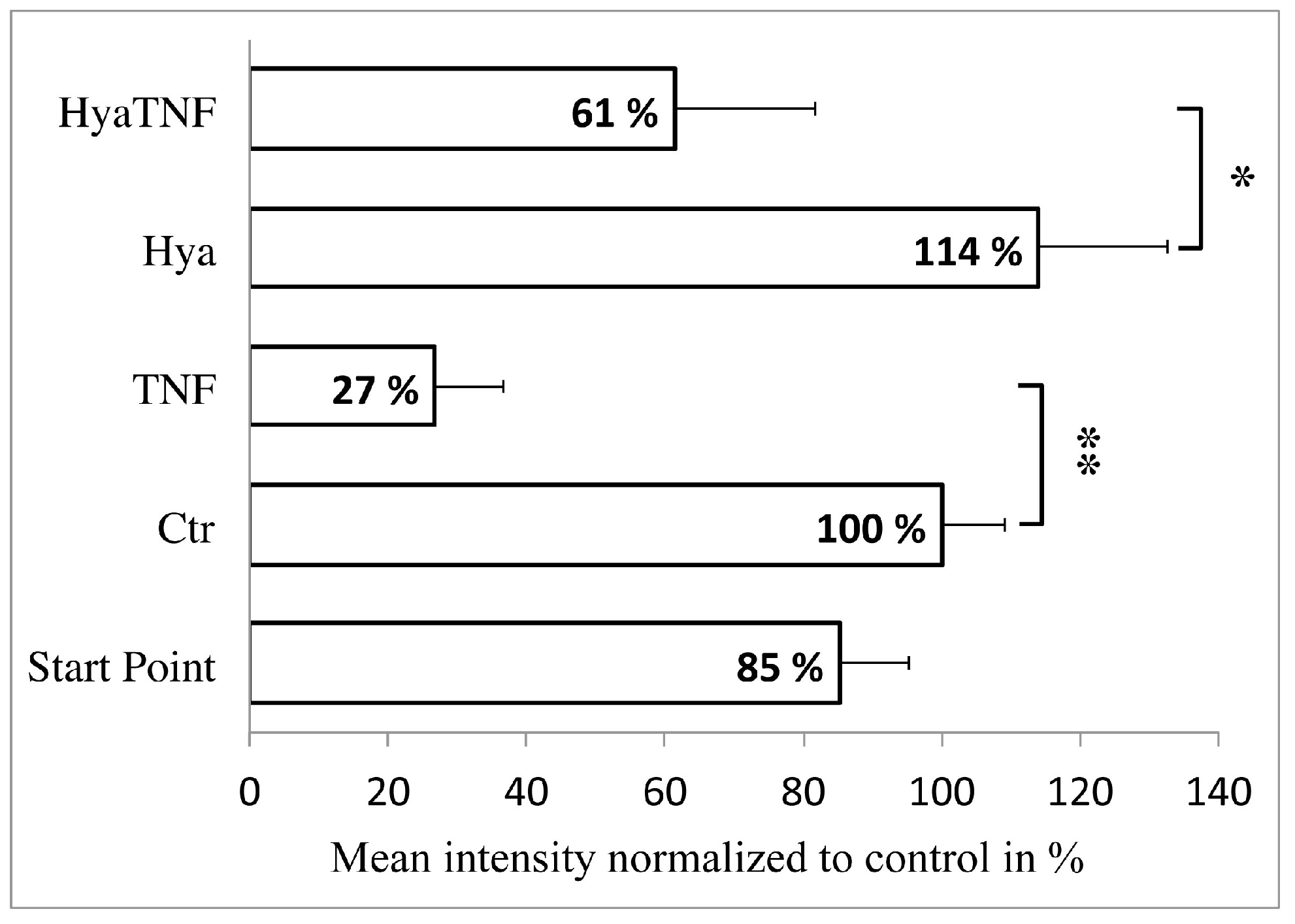
Ijms Free Full Text Hyaluronic Acid Influence On Normal And Osteoarthritic Tissue Engineered 96600


