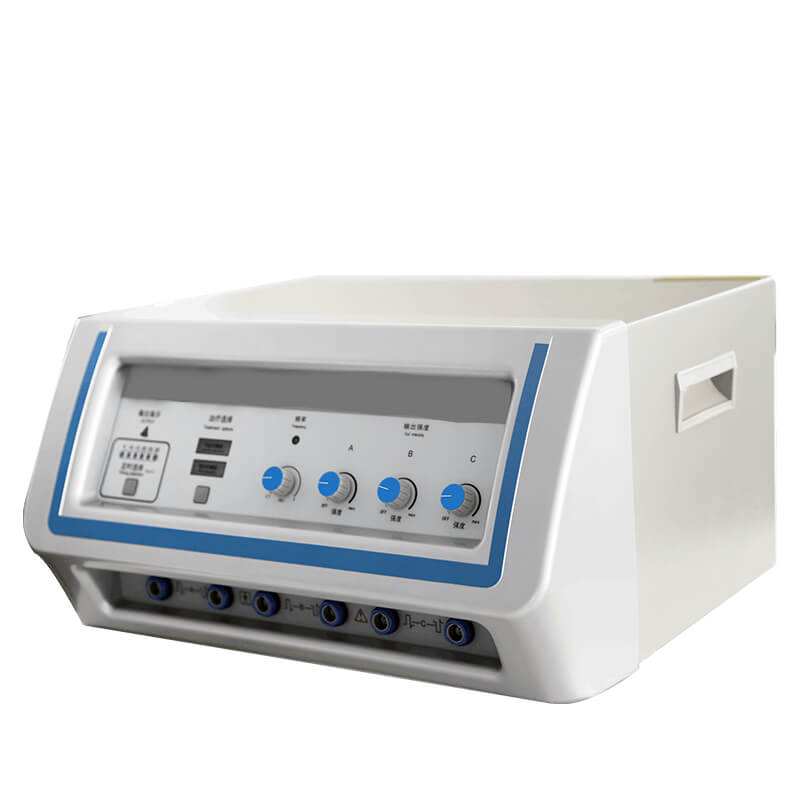
Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation combined with early rehabilitation therapy on mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective randomized controlled study, BMC Pulmonary Medicine
Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation combined with early rehabilitation therapy on mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective randomized controlled study, BMC Pulmonary Medicine
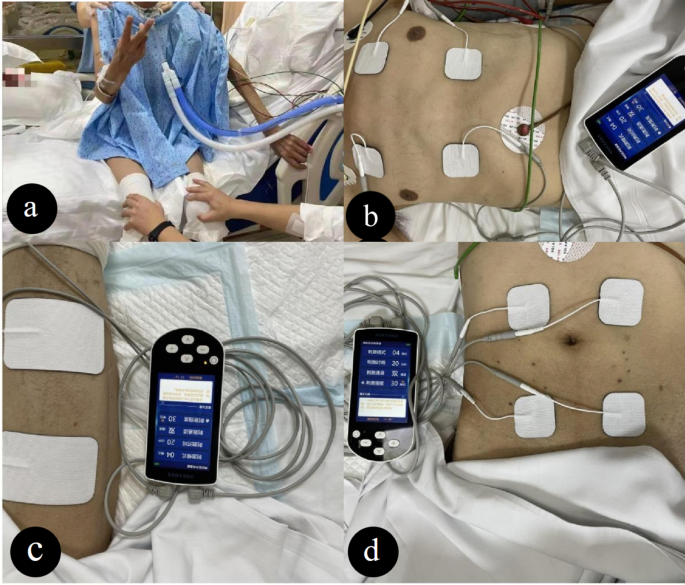
Background This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) blended with early rehabilitation on the diaphragm and skeletal muscle in sufferers on mechanical ventilation (MV). Method This is a prospective randomized controlled study. Eighty patients on MV for respiratory failure were divided into a study group (40 cases) and a control group (40 cases) randomly. The study group adopted a treatment method of NMES combined with early rehabilitation and the control group adopted the method of early rehabilitation only. The diaphragmatic excursion (DE), diaphragmatic thickening fraction (DTF), variation of thickness of intercostal muscles (TIM), variation of thickness of rectus abdominis (TRA), and variation of the cross-sectional area of rectus femoris (CSA-RF) were measured to evaluate the therapeutic effect by ultrasound before and after intervention at the first day of MV, the 3rd and 7th day of intervention and the day discharged from ICU. Results No significant difference was found in the general demographic information and ultrasound indicators between the two groups before treatment (all P > 0.05). After treatment, the variation of DTF (0.15 ± 0.05% vs. 0.12 ± 0.04%, P = 0.034) was significantly higher in the study group than that in the control group on the day discharged from ICU. The variation of TRA (0.05 ± 0.09% vs. 0.10 ± 0.11%, P = 0.029) and variation of CSA-RF (0.13 ± 0.07% vs. 0.19 ± 0.08%, P < 0.001) in the study group were significantly lower than that in the control group. The duration of MV in the study group was significantly shorter than that in the control group [109.5 (88.0, 213.0) hours vs. 189.5 (131.5, 343.5) hours, P = 0.023]. The study group had better muscle strength score than the control group at discharge (52.20 ± 11.70 vs. 44.10 ± 15.70, P = 0.011). Conclusion NMES combined with early rehabilitation therapy is beneficial in reducing muscle atrophy and improving muscle strength in mechanically ventilated patients. This treatment approach may provide a new option for patients to choose a rehabilitation program; however, more research is needed to fully evaluate the effectiveness of this treatment option.

A randomized, crossover, placebo controlled, double-blind trial of the effects of tiotropium-olodaterol on neuromuscular performance during exercise in COPD

PDF] Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for Intensive Care Unit–Acquired Weakness: Protocol and Methodological Implications for a Randomized, Sham- Controlled, Phase II Trial
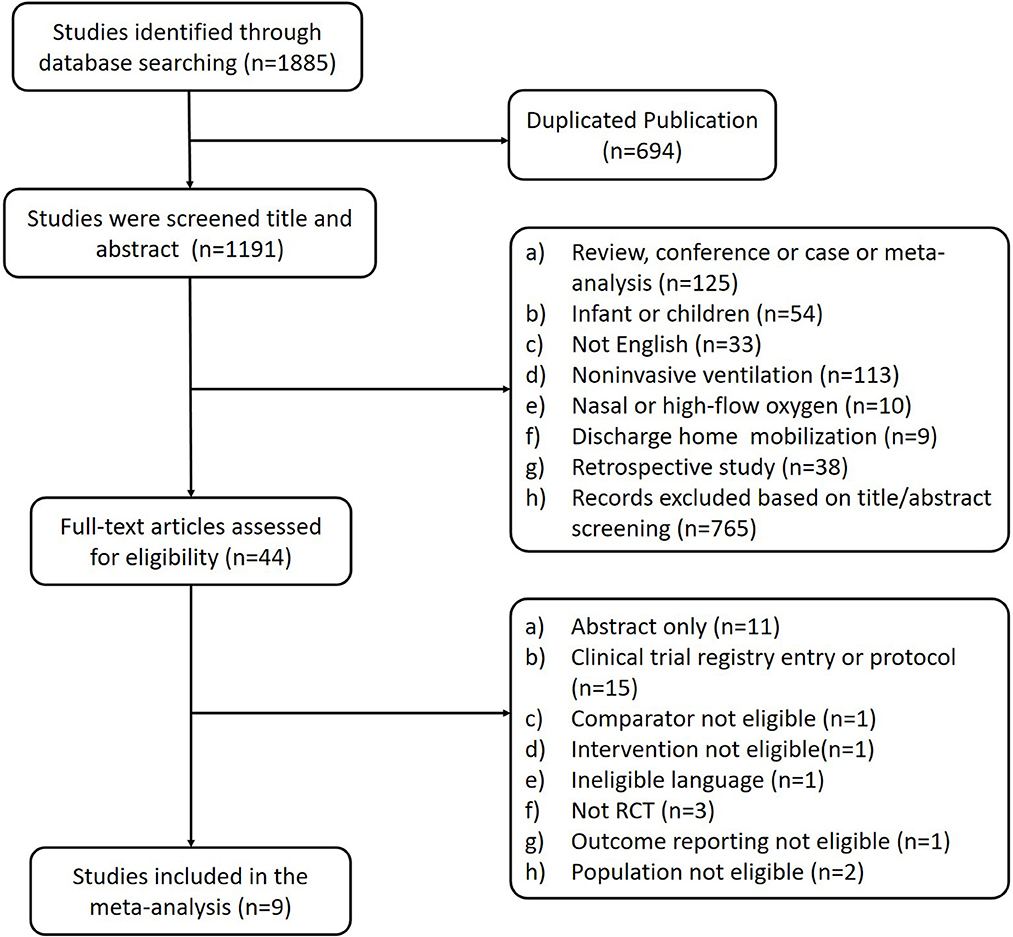
Frontiers The effects of early mobilization in mechanically ventilated adult ICU patients: systematic review and meta-analysis

Standard early rehabilitation and lower limb transcutaneous nerve or neuromuscular electrical stimulation in acute stroke patients: a randomized controlled pilot study - Hsiao-Ching Yen, Wen-Shiang Chen, Jiann-Shing Jeng, Jer-Junn Luh, Ya-Yun Lee

Prevention of Muscle Atrophy in ICU, PDF, Intensive Care Unit

Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for preventing skeletal-muscle weakness and wasting in critically ill patients: a systematic review – topic of research paper in Medical engineering. Download scholarly article PDF and read for free

Efficacy and safety of neuromuscular electrical stimulation in the prevention of pressure injuries in critically ill patients: a randomized controlled trial, Annals of Intensive Care

Neuromuscular electrical stimulation in mechanically ventilated patients: A randomized, sham-controlled pilot trial with blinded outcome assessment - ScienceDirect

Functional electrical stimulation-assisted cycle ergometry in the critically ill: protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials

Efficacy of neuromuscular electrical stimulation in patients with COPD followed in intensive care unit - Akar - 2017 - The Clinical Respiratory Journal - Wiley Online Library
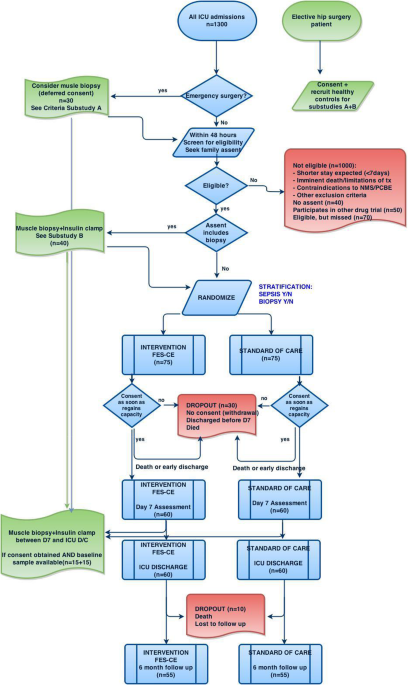
Functional electrical stimulation-assisted cycle ergometry in the critically ill: protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials

Early mobilisation within 72 hours after admission of critically ill patients in the intensive care unit: A systematic review with network meta-analysis - ScienceDirect
(PDF) Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation of the Quadriceps and Diaphragm in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
PDF) Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation combined with early rehabilitation therapy on mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective randomized controlled study


